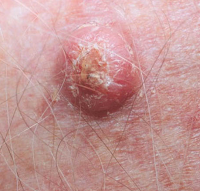
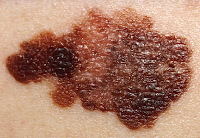
Skin neoplasms are skin growths with differing factors and differing levels of malignance. The three most frequent dangerous skin cancers are basal cell cancer, squamous cell cancer, and melanoma, each of which is named after the type of skin cell from which it develops. Skin cancer commonly grows in the epidermis (the outermost layer of skin), so a tumor is usually appears observed. This makes most skin cancers perceptible in the beginning. In contrast to a lot of various cancers, such as those coming initially from in the lung, pancreas, and stomach, only a little section of those impacted will really die of the condition. In reality, however it can be disfiguring, skin cancer is seldom dangerous, excepting melanoma.
Skin cancer is the most frequently identified type of cancer, its mixed occurrence exceeding lung, breasts, colorectal, and prostate cancer. Melanoma is less frequent than both basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, but it is the most severe, for illustration, in the UK there are actually 9,500 new cases of melanoma every year, causing in 2,300 fatalities. It is the most usual cancer in the youthful people (15 – 25 age group). Most cases are triggered by long intervals of coverage to the sun. Non-melanoma skin cancers are the most typical skin cancers. The most of these are basal cell carcinomas. These are generally localised growths triggered by high cumulative coverage to the sun and do not tend to multiply.
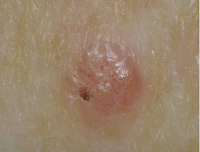 1. Basal Cell Carcinoma
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma